Study shows Magazines are the medium of engagement
-
From the 2011/12 Magazine Media Factbook, published by the The Association
of Magazine Media, Magazines are the *medium of engagement*. "Magazines
continu...
Thursday, December 3, 2009
Kentucky Doc Magazine is committed to promoting our region’s products, services and professionals that physicians and physician practices have at their disposal. Delivered to your practice on a monthly basis, we are your personalized resource. Is there a service, product, professional or event you’d like to know more about? Please feel free to contact, Kris Martin, Editor of Kentucky Doc Magazine. Email: whosyouraudience@yahoo.com
Swine Flu Vaccination
H1N1 vaccination clinics will be held Saturday, December 5 from 8:30 a.m.-12:30 p.m. at two locations:
*Bryan Station High School, 201 Eastin Road
*Southland Christian Church (Building F), 5001 Harrodsburg Road(co-sponsored by the Jessamine County Health Department)
The health department will continue to post the latest updated information on the clinics on its Flu Hotline, 288-7529, and online at www.LexFluCrew.com.
Tuesday, December 1, 2009

Patients with congenital heart disease will have a chance at a treatment without a major open heart surgery. Cardiologists at the Rush University Medical Center has developed a minimally-invasive transcatheter valve replacement. Patients involved in a clinical trial had this implant, and are presently recovering. This gives hope to patients that would otherwise undergo multiple open heart surgeries. The valve replacement procedure uses a bovine pericardial heart valve that is compressed into a balloon as small as a pencil, threaded from a major vein in the leg into the circulatory system, and is deployed across the pulmonary valve.
Real Fake Leg

Prosthetic legs have evolved to lightweight and more friendly. The old prosthetics were designed just to allow patients to stand with both legs, but walking and climbing the stairs were difficult, and running was impossible. Then bendable prosthetics were developed. Now a prosthetic that looks like the real thing gives people who lost their legs a better chance to live normal lives, and wear clothes that they otherwise would not wear with the old cyborg-like prosthetics.
One particular design was called LISA, which stood for lightweight, inconspicuous, shapely and active. Running is now possible, and women can even wear shoes with heels, as the ankles can be adjusted with a button.
One particular design was called LISA, which stood for lightweight, inconspicuous, shapely and active. Running is now possible, and women can even wear shoes with heels, as the ankles can be adjusted with a button.
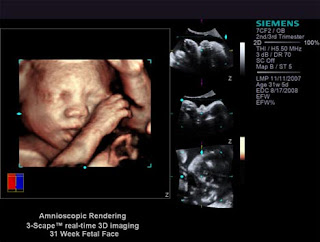
Siemens has formed a partnership with video graphics company NVIDIA to create a 3D visualization system for expecting parents to get up and close with their fetus. The system uses a PC to process images from a Siemens ACUSON S2000 and NVIDIA's 3D Vision glasses to produce stereo visuals of the child. The system is currently on show at the RSNA 2009 conference in Chicago.

The clinical images, obtained with the ACUSON S2000™ ultrasound system, are further enhanced using Amnioscopic Rendering, a Siemens- exclusive technology that produces photo-realistic 3D images of the fetus. While conventional 3D ultrasound technologies use two-dimensional monitors for the evaluation of 3D images, utilizing NVIDIA 3D Vision technology, users can experience 3D images in real 3D, vastly improving the overall ultrasound experience.
The experience was demonstrated at the Radiological Society of North America’s Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, which showcases the world’s most cutting-edge science, education, and technology in radiology and medical imaging. Siemens’ fourSight Workplace, which manages clinical images, clips and 3D/4D volume data to enhance department workflow, utilizes a Dell Precision T5500 workstation driven by an NVIDIA Quadro FX 3800 professional graphics card, a Samsung 2233RZ 22-inch, 3D Vision-ready LCD, and NVIDIA 3D Vision glasses to demonstrate how patients and their doctors can view remarkable, high-resolution, three-dimensional sonograms in true 3D.
The experience was demonstrated at the Radiological Society of North America’s Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, which showcases the world’s most cutting-edge science, education, and technology in radiology and medical imaging. Siemens’ fourSight Workplace, which manages clinical images, clips and 3D/4D volume data to enhance department workflow, utilizes a Dell Precision T5500 workstation driven by an NVIDIA Quadro FX 3800 professional graphics card, a Samsung 2233RZ 22-inch, 3D Vision-ready LCD, and NVIDIA 3D Vision glasses to demonstrate how patients and their doctors can view remarkable, high-resolution, three-dimensional sonograms in true 3D.
Quad buffered stereo is enabled with 3D stereoscopic glasses and displays, driven by NVIDIA Quadro FX high-end and ultra-high end solutions.
Public Health Marks World AIDS Day - December 1.
 The Kentucky Department for Public Health is recognizing Dec. 1 as World AIDS Day, an observance set aside on the same day each year to raise HIV and AIDS awareness, increase HIV education and fight HIV stigma and discrimination.
The Kentucky Department for Public Health is recognizing Dec. 1 as World AIDS Day, an observance set aside on the same day each year to raise HIV and AIDS awareness, increase HIV education and fight HIV stigma and discrimination.This year’s World AIDS Day theme is Universal Access and Human Rights. The theme’s focus is ensuring access to HIV prevention services, medication and timely, effective HIV treatment and care services to infected people.
More than 1 million people are living with HIV in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates someone in the U.S. gets infected with HIV every 9.5 minutes, amounting to 56,300 new infections annually. While great strides have been made in providing access to HIV/AIDS services, a significant number of infected people who are in need of antiretroviral therapy and other treatment do not have access to it.
In 2007, up to 30 percent of those diagnosed with HIV/AIDS in Kentucky were aware of their status but not receiving regular primary health care. Additionally, CDC estimates that 21 percent of those living with HIV disease are unaware they are infected, and hence do not receive care. African-Americans account for 48.6 percent and Hispanics 18 percent of HIV-positive people who are unaware of their status and respectively have nine times and three times the rate of undiagnosed HIV infections than Caucasians.
“The Kentucky Department for Public Health HIV/AIDS Branch continues to work diligently to reduce the number of new HIV infections, increase the proportion of HIV-infected people in Kentucky who are aware of their status, and ensure that people living with HIV and AIDS have access to prevention, care and support services,” said Sigga Jagne, manager of the DPH HIV/AIDS Branch. “Awareness and public education are very important pieces of what we do.”
The HIV/AIDS Branch is particularly focused on education and outreach among racial/ethnic minorities and men who have sex with men (MSM) due to the disproportionate impact on these communities.
As of Dec. 31, 2008, 5,015 AIDS cases have been reported in Kentucky since Public Health began tracking cases. According to DPH, 46 percent of cases were MSM, 37 percent were African-American, and 7 percent were Hispanic. Additionally, 46 percent were residing in the KIPDA area development district (which includes Jefferson County).
The HIV/AIDS Branch, in collaboration with local health departments and many community-based organizations, provides free or low-cost HIV testing. To mark World AIDS Day, many of these agencies will offer free “rapid tests” at events and hold candlelight vigils to raise awareness of HIV issues and remember those who have died from AIDS.
To find out about events and activities going on in your community throughout December, please contact the HIV/AIDS Branch’s prevention program at (502) 564-6539 or 1-800-420-7431.
For more information about HIV/AIDS and World AIDS Day, please visit http://chfs.ky.gov/dph/epi/hivaids.htm or http://www.worldaidscampaign.org/.
Tuesday, November 24, 2009
Gene increases effectiveness of drugs used to fight cancer and allows reduction in dosage
 Researchers at the University of Granada have found a suicide gene, called 'gene E', which leads to the death of tumour cells derived from breast, lung and colon cancer, and prevents their growth. The importance of this new gene is that its use to fight cancer can reduce the potent drugs that are currently used, so that could mean more effective treatment for cancer. This research was conducted by Ana Rosa Rama Ballesteros, from the Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology at the University of Granada. Its aim was to study the possibility of reducing the dosage of drugs currently administered to cancer patients using combination therapy with suicide gene E. Scientists from the UGR have shown that the bacteriophage phiX174 killer gene called E, can be used to induce death in tumour cells. So far, attempts to use many chemotherapeutic (cytotoxic) agents similar to the E gene have shown severe limitations resulting from their toxicity and their poor affinity with the tumour.
Researchers at the University of Granada have found a suicide gene, called 'gene E', which leads to the death of tumour cells derived from breast, lung and colon cancer, and prevents their growth. The importance of this new gene is that its use to fight cancer can reduce the potent drugs that are currently used, so that could mean more effective treatment for cancer. This research was conducted by Ana Rosa Rama Ballesteros, from the Department of Anatomy and Human Embryology at the University of Granada. Its aim was to study the possibility of reducing the dosage of drugs currently administered to cancer patients using combination therapy with suicide gene E. Scientists from the UGR have shown that the bacteriophage phiX174 killer gene called E, can be used to induce death in tumour cells. So far, attempts to use many chemotherapeutic (cytotoxic) agents similar to the E gene have shown severe limitations resulting from their toxicity and their poor affinity with the tumour.The results of this research suggest the possibility of reducing the concentration of chemotherapeutic agents in current use with cancer patients. Thus, in lung cancer cell line A-549, scientists from the UGR achieved a 14% inhibition of tumour growth and reduced by 100 times the dose of Paclitaxel agent when it was combined with gene E. In the case of colon cancer, the results were similar. However, the most relevant fact was found in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7, in which the dose of the chemotherapeutic agent, doxorubicin, was reduced by 100 times, reaching up to a 21% greater inhibition of tumour proliferation when combined with gene E. Currently, researchers from the UGR are in the process of obtaining a patent for gene E.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)






